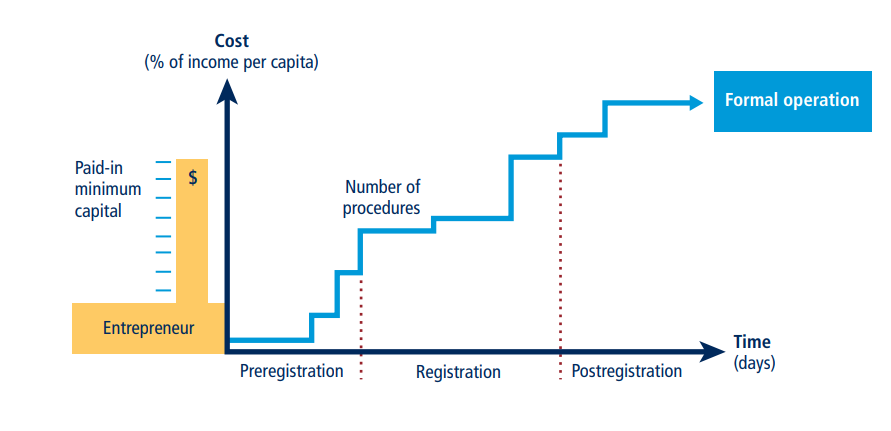
This topic measured the number of procedures, time, cost and paid-in minimum capital requirement for a small- to medium-size limited liability company to start up and formally operate in each economy’s largest business city. To make the data comparable across 190 economies, Doing Business used a standardized business that is 100% domestically owned, has a start-up capital equivalent to 10 times the income per capita, engages in general industrial or commercial activities and employs between 10 and 50 people one month after the commencement of operations, all of whom are domestic nationals. The starting a business indicators considered two cases of local limited liability companies that are identical in all aspects, except that one company is owned by five married women and the other by five married men. The overall score for starting a business is the average of the scores obtained for each of the component indicators. The most recent round of data collection for the project was completed in May 2019. See the methodology and video for more information.
See information about entrepreneurial activity - including firm entry rates and gender-disaggregated statistics - in the Entrepreneurship Database.